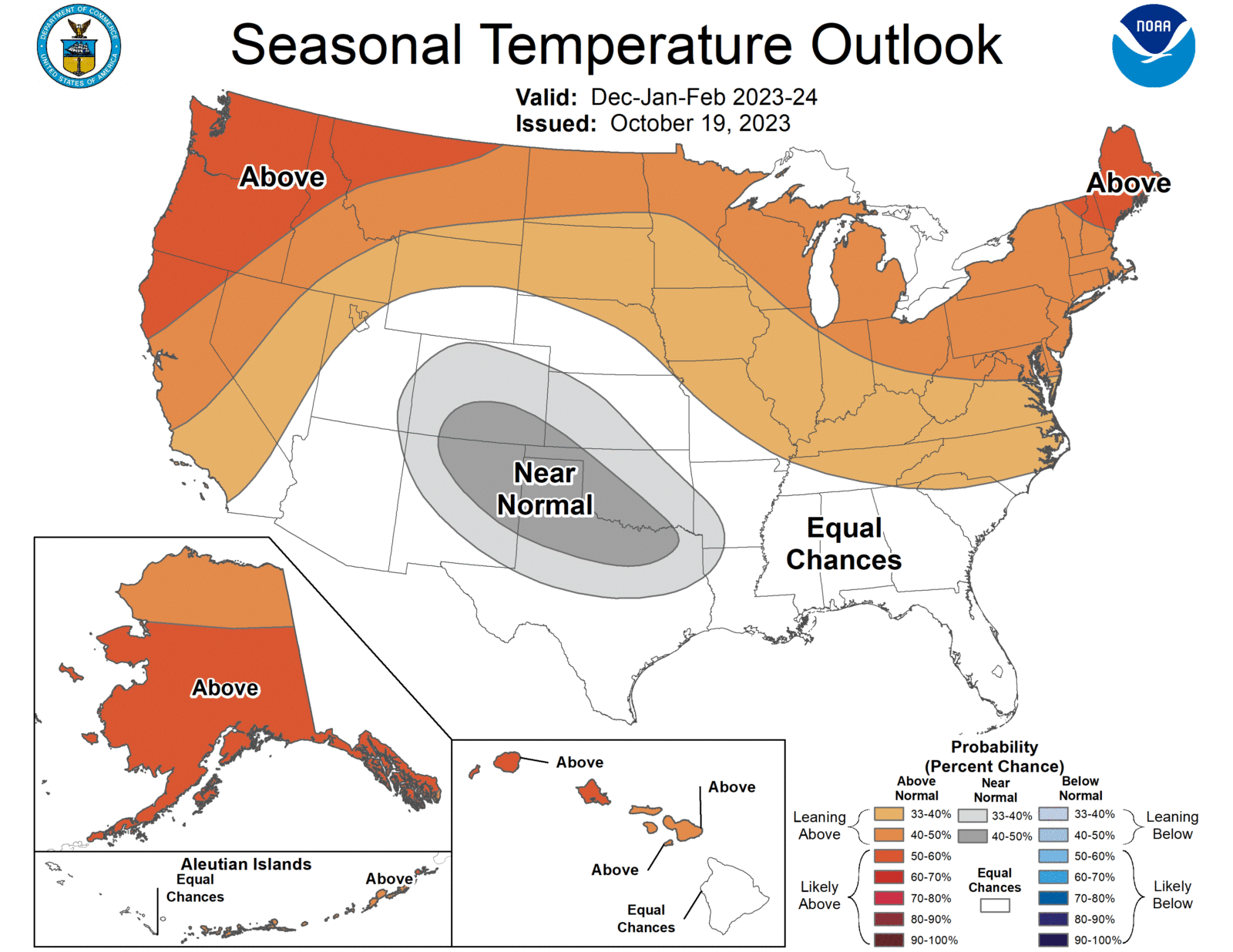
This year, El Nino is in place heading into winter for the first time in four years, driving the outlook for warmer-than-average temperatures for the northern tier of the continental United States, according to NOAA’s U.S. Winter Outlook released this week by the Climate Prediction Center — a division of the National Weather Service.
“These outlooks provide critical guidance on the upcoming season for many industries and sectors of our economy, from energy producers to commodities markets to agricultural interests to tourism,” said Sarah Kapnick, NOAA chief scientist. “With a strengthening El Nino and more potential climate extremes in an already record-breaking year, we’re lucky to have scientists like those at the Climate Prediction Center helping to build a Weather and Climate-Ready Nation by providing critical operational seasonal climate predictions.”
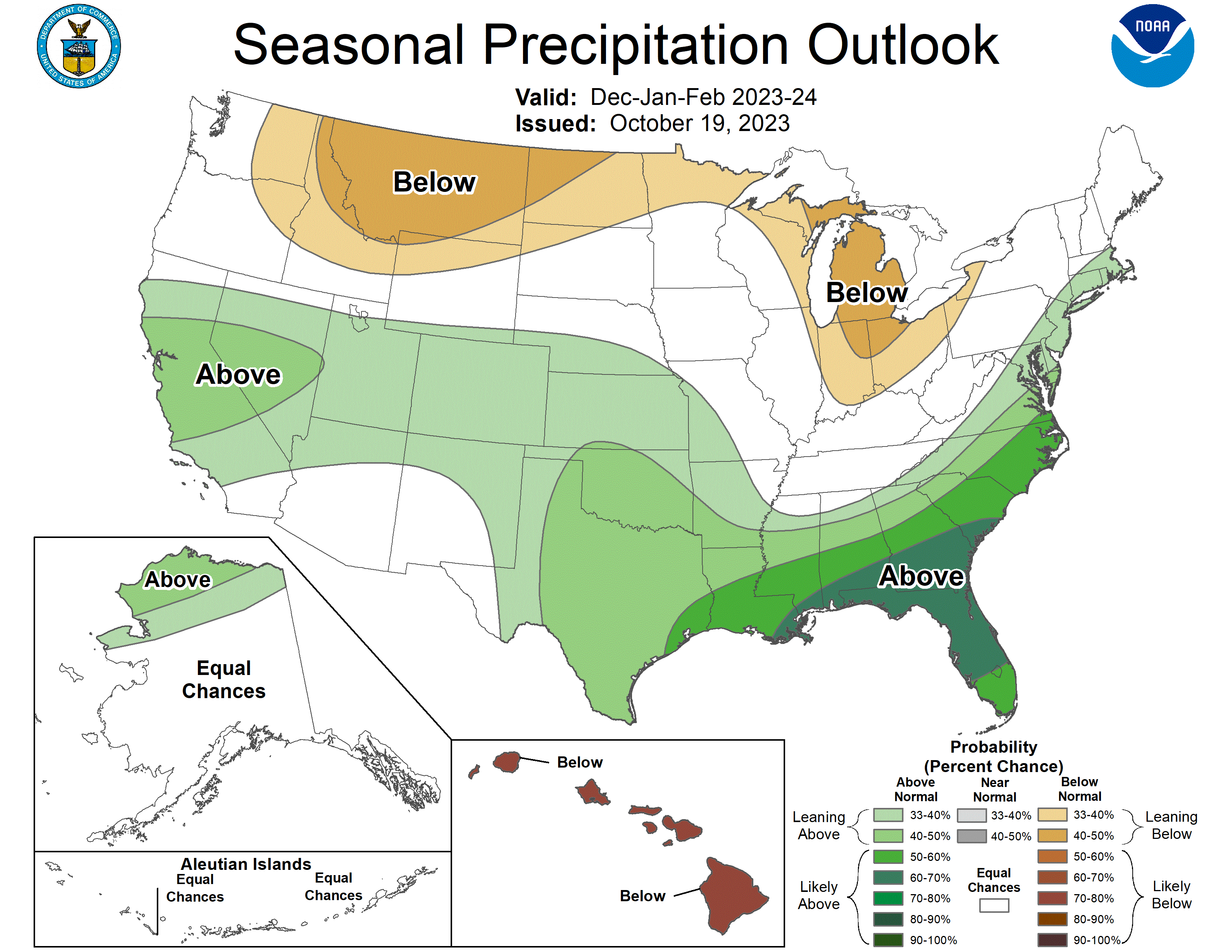
From December through February, NOAA predicts wetter-than-average conditions for northern Alaska, portions of the West, the southern Plains, Southeast, Gulf Coast and lower mid-Atlantic and drier-than-average conditions across the northern tier of the U.S., especially in the northern Rockies and High Plains and near the Great Lakes.
“An enhanced southern jet stream and associated moisture often present during strong El Nino events supports high odds for above-average precipitation for the Gulf Coast, lower Mississippi Valley and Southeast states this winter,” said Jon Gottschalck, chief of the Operational Prediction Branch of the Climate Prediction Center.
NOAA forecasters, in collaboration with the National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS), continue to monitor extreme, ongoing drought conditions that have persisted through the southern and central U.S. and worsening drought in Hawaii.
“According to the Oct. 17 U.S. Drought Monitor, a third of the country, including Puerto Rico, is in drought,” said Brad Pugh, operational drought lead with NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center. “During late October, heavy precipitation is likely to result in drought improvement for the central U.S. El Nino with its enhanced precipitation is expected to provide drought relief to the southern U.S. during the next few months.”
Warmer-than-average temperatures are favored across the northern tier of the U.S. and much of the Far West.
The greatest odds for warmer-than-average conditions are in Alaska, the Pacific Northwest and northern New England.
Near-normal seasonal mean temperatures are most likely for a region from the south-central Rockies to the southern Plains.
Remaining areas fall into the category of equal chances for below-, near-, or above-average seasonal mean temperatures.
Wetter-than-average conditions are most likely in northern Alaska, some areas of the West from parts of California to the south-central Rockies, the southern Plains, Gulf Coast, Southeast and lower mid-Atlantic.
The greatest odds for drier-than-average conditions are forecast in portions of the northern Rockies and central Great Lakes region, especially for Michigan and northern Ohio and Indiana.
Much of the central portion of the U.S. falls into the category of equal chances for below-, near-, or above-average seasonal total precipitation.
Widespread extreme to exceptional drought continues to persist across much of the South, and portions of the central U.S.

Drought conditions are expected to improve across the Southeast, the Gulf Coast (including the lower Mississippi Valley), and Texas due to the expected wetter-than-average forecast.
Drought conditions are expected to persist for the northern Rockies, northern Great Plains, and portions of the desert Southwest this winter.
Drought development could occur in the interior Pacific Northwest given the chance for drier-than-average conditions.
Drought is likely to persist or develop across Hawaii.
NOAA’s seasonal outlooks provide the likelihood that temperatures and total precipitation amounts will be above-, near- or below-average, and how drought conditions are anticipated to change in the months ahead. The outlook does not project seasonal snowfall accumulations as snow forecasts are generally not predictable more than a week in advance.
NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center updates the three-month outlook each month. The next update will be available November 16.
This winter, NOAA will implement a series of upgrades and improvements. In November, the experimental Probabilistic Winter Storm Severity Index (WSSI-P) will become operational. The product, says the agency, will enhance communication with external partners, media and the general public by graphically depicting the likelihood of potential societal impacts due to expected winter hazards over a 7-day period. This is complemented by a version of the Winter Storm Severity Index (WSSI) based on the official National Weather Service forecast of the most likely conditions over the next three days.
NOAA’s Weather Prediction and Climate Prediction Centers will continue to use Winter Key Messages, which highlight the agency’s most essential information for upcoming winter weather, including extreme cold and heavy snow potential. These can be found under “Top Stories” on the Weather Prediction Center’s and Climate Prediction Center’s websites.
This winter, NOAA will complete its implementation of Impact-Based Warning Tags for Snow Squall Warnings. Snow Squall Warnings are warnings issued for short duration intense bursts of snow and wind leading to whiteout visibility and possible flash freezes on roads. To distinguish high-impact snow squalls, the National Weather Service will issue impact-based Snow Squall Warnings using the “Significant” tag for events that pose a substantial threat to safe travel. Wireless Emergency Alerts, emergency messages sent by authorized government alerting authorities through wireless carriers, will be limited to only high-impact Snow Squall Warnings with the Snow Squall Impact Tag of “Significant.”